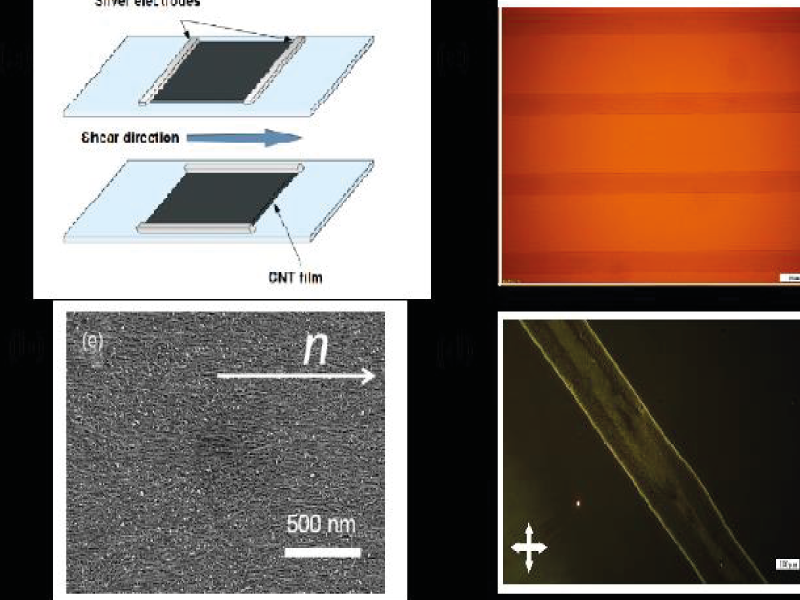
Most of the potential applications in carbon nanotubes and graphene-based composites require suitable methods for making aligned assemblies on a large scale. Liquid crystal ordering is an opportunity to develop such materials and applications [1]. In this talk, we will present a review of our recent results in the preparation and characterization of lyotropic liquid crystals based on concentrated aqueous suspensions, stabilized by surfactants, of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) or reduced graphene oxide (RGO). In the first part we will focus on anisotropic conductive films, which are prepared by shearing and drying the LC. In particular, we will show how the electrical conductivity anisotropy increases with the order parameter of the nematic liquid crystal. The order parameter can be tuned by controlling the length and entanglement of the nanotubes [1-3]. In the second part we present recent results on the morphology and anisotropy of thin conductive lines of SWCNT, inkjet-printed. Its morphology can be tuned from rail track to quasi-continuous lines by increasing nanotube concentration and drop density
YACHAY TECH SCHEDULE
Liquid crystals based on carbon nanotubes and graphene: synthesis and applications

Camilo Zamora Ledezma, Ph.D.
Most of the potential applications in carbon nanotubes and graphene-based composites require suitable methods for making aligned assemblies on a large scale. Liquid crystal ordering is an opportunity to develop such materials and applications [1]. In this talk, we will present a review of our recent results in the preparation and characterization of lyotropic liquid crystals based on concentrated aqueous suspensions, stabilized by surfactants, of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) or reduced graphene oxide (RGO). In the first part we will focus on anisotropic conductive films, which are prepared by shearing and drying the LC. In particular, we will show how the electrical conductivity anisotropy increases with the order parameter of the nematic liquid crystal. The order parameter can be tuned by controlling the length and entanglement of the nanotubes [1-3]. In the second part we present recent results on the morphology and anisotropy of thin conductive lines of SWCNT, inkjet-printed. Its morphology can be tuned from rail track to quasi-continuous lines by increasing nanotube concentration and drop density